Distinguishing Delirium and Dementia
Delirium and dementia can be distinguished in the ED setting
Understanding the differences is key
Delirium and dementia can be distinguished in the ED setting, though it can be challenging. Understanding the key characteristics of delirium and dementia can help emergency personnel distinguish between the two.
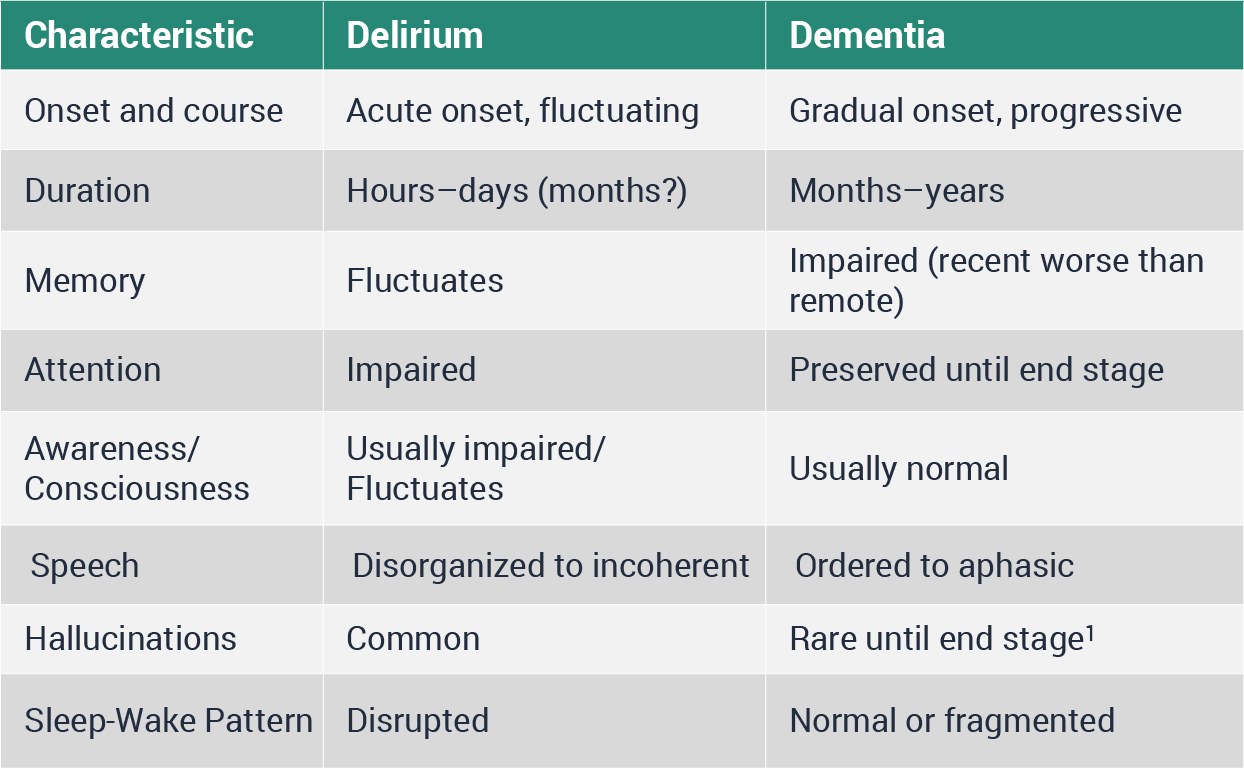 1 exception for Lewy body dementia
1 exception for Lewy body dementiaNOTE:
- Delirium is primarily a disorder of attention
- Dementia is primarily a disorder of cognition
- Delirium is characterized by an abrupt onset and may fluctuate
- Short duration of ED care episode can impact ability to recognize acute changes in cognition and/or fluctuations
- Collateral information can be critical in this respect
- Hallucinations are common in delirium but rare in dementia until end-stage
- Exception: hallucinations a defining feature of Lewy body dementia
- Alterations in sleep-wake cycle and disorganized thought and speech are common in delirium but rare in dementia
Patients with dementia are at increased risk of delirium (delirium superimposed on dementia, or DSD) which can make diagnosis more challenging.
An in-depth review of screening tools that can aid in the diagnosis of delirium in the ED setting is provided in the next lesson–Screening for Delirium in the Emergency Department.
References
Kennedy, M. Delirium in the Emergency Department: Diagnosis, Evaluation, and Management. In: Brown D, editor. Scientific American emergency medicine. Hamilton (ON): Decker Intellectual Properties; April 2018. DOI: 10.2310/7900.4709. Available at: http://www.deckerip.com.
